August 2017 National Right To Work Newsletter Summary
Go here to read the August 2017 National Right to Work Newsletter.
Go here to read the August 2017 National Right to Work Newsletter.
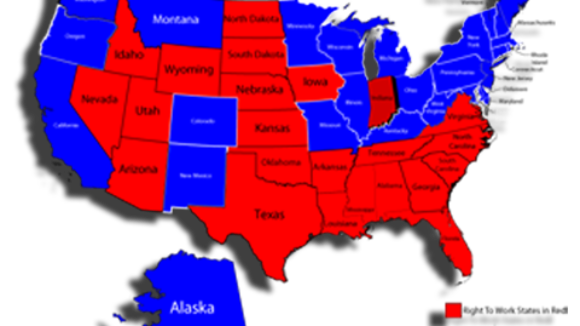
States Seeking a 'Brain Gain' Should Bar Compulsory Union Dues The nine states with the greatest 2000-2010 gains in their college-educated adult populations all protect the Right to Work. Of the nine states with the smallest gains, only Hurricane Katrina-devastated Louisiana does so. (Source: November-December 2011 National Right to Work Committee Newsletter) Federal data on the American workforce and employment and unemployment rates show that, even with our country struggling through the most severe recession in decades and a so-far anemic recovery, employer demand for college-educated employees has continued to rise at a surprisingly rapid clip. From 2000 to 2010, the total population of the U.S., aged 25 and over, grew by 12.1%, but the number of people in that age bracket with at least a bachelor's degree grew by 29.3%. And in October 2011, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the labor force participation rate for civilians aged 25 or older with one or more higher-education degrees was 76.4% (not seasonally adjusted), barely lower than it was before the recession started. That same month, the nationwide unemployment rate for the pool of 47.3 million college-educated adults 25 or over was just 4.2%, well under half the average for the workforce as a whole. The bottom-line significance of these data is that employers across the country typically have more difficulty finding a qualified college-educated person to fill a position than a college-educated person has finding a good job. Of course, not everyone who holds a bachelor's degree and is in the work force is doing well economically. But generally speaking there is still a "seller's market" for college-educated labor in America today. Furthermore, many businesses that sustain large numbers of jobs for people with associate's degrees, high school diplomas, or less education also require a substantial number of college-educated people to operate smoothly. Therefore, the rate at which a state is gaining college-educated people, relative to the national average, is in itself a good indication of how successful the state is in creating and retaining good jobs. 'Highly Educated Employees, Like Other Employees, Benefit From Right to Work Laws'

From Missouri State Sen. Robert N. Mayer's Op-Ed in the Southeast Missiourian 'Right to work' equals jobs: More than 280,000 Missourians are out of work. The alarm is sounding and we should all hear the wake-up call that now is the time to put all the pieces in place so Missouri can truly compete for jobs. Currently, Missouri is missing out on new jobs because companies are drawn to other states with better worker protection laws. Fifty percent of manufacturers refuse to consider Missouri as a place to locate new jobs because we have no protections against forced unionization of our workers -- that's according to testimony given to the Senate General Laws Committee by Mark Sweeney. Sweeney is a site location consultant who works to find new plant sites for both domestic and foreign manufacturing companies. He says Missouri is off the radar for 50 percent of his clients, plus the rest consider right-to-work laws when weighing which state they will choose. Not having right-to-work has cost us in many ways. First, Missouri is losing a congressional seat due to the most recent census data. That data shows businesses with jobs and the workers who take them are fleeing to states with worker protection laws. Non-right-to-work states lost a total of nine congressional seats and, due to population shifts, right-to-work states gained 11. This session we have the opportunity to correct this wrong by bringing beneficial jobs to Missouri while keeping hard-working citizens in our state. Second, we have underperformed compared with the six of our eight neighboring states that are right-to-work states. All those states have lower unemployment rates than Missouri. Tennessee, the only one with a comparable rate to ours, gained jobs in 2010 while Missouri lost jobs. Plus, data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics shows unemployment is lower in the 22 states that have adopted right-to-work laws. In the last decade, those states have added 1.5 million private sector jobs, while non-right-to-work states have lost 1.8 million jobs. With more than 160,000 jobs lost in our state since June 2008, we cannot afford to stand by and not take action.