Teachers Union Dues Fund Everything But Better Education
The Wall Street Journal continues to examine big labor’s ability to use coercive forced-union dues money…
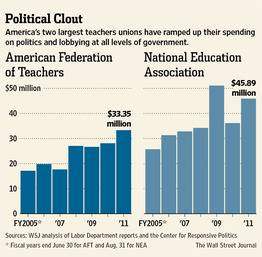
The Wall Street Journal continues to examine big labor’s ability to use coercive forced-union dues money…

The power of the union bosses in California was on full display for the world to see when the legislature killed a bill that would have made it easier to investigate and fire teachers accused of serious misconduct. “Legislation to…

Big Labor History Flashback The American Federation of Teachers, AFL-CIO (AFT) which benefits dramatically from government employee forced dues at one time was opposed to representing both administrators and teachers. From the New York Times, Aug 19, 1959 report from…

Big Labor History Flashback The American Federation of Teachers, AFL-CIO (AFT) which benefits dramatically from government employee forced dues at one time was opposed to representing both administrators and teachers. From the New York Times, Aug 19, 1959 report from…

In New York state, a teacher who showed up late for class 101 times in a single school year and left early 47 times is still on the job. Thanks to the monopoly bargaining power of the teacher’s union, she…
Some bills making their way through the Florida legislature are striking fear into the union bosses in Florida because it threatens big labor’s access to the wallets of teachers. One bill would would bar any public union from automatically…

Government employee union woes are being felt from California to Maryland. George W. Liebmann, executive director of the Calvert Institute for Policy Research Inc., lists several problems in Maryland in his Baltimore Sun op-ed: Marylanders need instruction in how entrenched the state's teachers' unions are: 1. Eleven counties, including all the more populous ones, allow unions to collect "agency fees" from nonmembers, generating huge war chests. While in theory such fees are not supposed to be used for political purposes, a famous [NRTW] lawsuit in Washington state revealed that nearly 80 percent of "agency fees" are in fact so used. 2. The State Board of Education has only qualified authority over teacher certification. A special board, eight of whose 24 members are named by unions and six of whom are from teachers' colleges, can only be over-ridden by a three-fourths vote of the State Board. 3. Under a law signed by Gov. Martin O'Malley last year, another special board, two of whose five members are named by unions, has the last word in resolving impasses in school labor negotiations. 4. Local union contracts impose maximums on the length of the school year, limitations originally derived from the needs of agricultural societies 5. Maryland's charter school law is one of the few that binds charter school teachers to union contracts, and it provides few checks against refusal of applications by self-protective county boards. Experimentation with "virtual schools" and distance learning is limited by a law binding employees to union contracts. 8. Contracts severely limit teacher attendance at PTA meetings, in some counties to two hours per year; and at post-school meetings, frequently to one hour a month. Evaluations and observations are severely limited; only a handful of teachers are ever found to be incompetent. 9. In all but three counties, third-party arbitrators, rather than the local board of education, are given the last word in grievance proceedings. There is a three-to-five step grievance procedure, making discipline of tenured teachers all but impossible. Out of a tenured force of more than 5,600, no more than two Baltimore City teachers were fired for cause, per year, between 1984 and 1990.
Teacher Unions Must Collect their Own Dues Governor Bob Riley speaks to a gathering of lawmakers and citizens before signing into law a series of sweeping anti-corruption reforms. Photo credit: Robin Cooper, Office of the Governor. Alabama’s News 13: “A…
Teacher Unions Must Collect their Own Dues Governor Bob Riley speaks to a gathering of lawmakers and citizens before signing into law a series of sweeping anti-corruption reforms. Photo credit: Robin Cooper, Office of the Governor. Alabama’s News 13: “A…