"Former Michigan Governor Jennifer Granholm Makes the Case for Right to Work Laws"
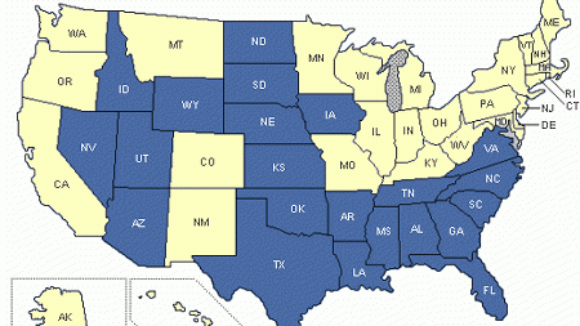
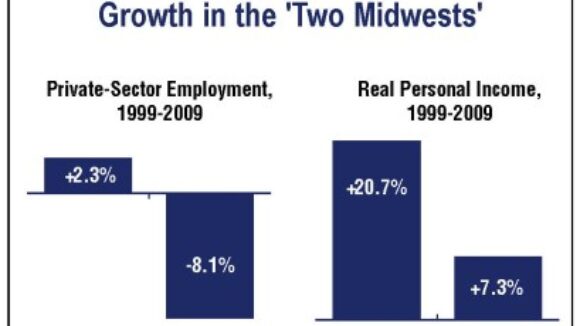
Matt Mayer of the Buckeye Institute debunks the long-term economic growth without Right To Work freedom is sustainable. Mayer uses a Columbus Dispatch reporter Joe Hatlett column that featured Former Michigan Gov. Jennifer Granholm to expose the fact that corporate welfare and reduced regulations ignore the “proverbial elephant in the room weighing down” compulsory union states like Indiana, Ohio, Illinois,, and Michigan. From Matt Mayer’s post: “With Michigan bleeding jobs and tax revenues, Granholm said she followed the corporate playbook in her attempt to close a huge state budget deficit and make Michigan more competitive. ‘In listening to the business community, I cut takes [sic] 99 times, and I ended shrinking government more than any state in the nation. In my two terms, I cut more by far than any state in the nation. And yet, we still have the highest unemployment rate. There was no correlation.’ Granholm conceded that streamlining business regulations and lowering taxes — Kasich’s economic recovery mantra — are helpful, but they aren’t a panacea…[l]abor costs, help with start-up costs and proximity to markets are other factors.” Hallett and Governor Granholm fail to mention why streamlining regulations and lowering taxes aren’t helping the northern states (located within 50 percent of the U.S. population and with low start-up costs) compete against the southern and western states. Instead, Hallett ignores the obvious answer and pleads for an end to corporate pork (with which we enthusiastically agree). The reason Michigan and Ohio can’t compete is that the southern and western states already have fewer regulations and lower taxes, so “catching up” with those states still leaves the proverbial elephant in the room weighing down the northern states. Plus, those states are also pushing for lower taxes and fewer regulations, so the northern states are perpetually behind them. The elephant, which Governor Granholm does hint at, is labor costs, or, more specifically, unionized labor costs (see: General Motors and the United Auto Workers). As I noted in Six Principles for Fixing Ohio, “Of course, tax and regulatory burdens also impact a state’s economy. Although many of the forced unionization states have heavy tax burdens and many of the worker freedom states have light tax burdens, some heavily taxed worker freedom states (Idaho, Nevada, and Utah) had the strongest sustained job growth from 1990 to today. Similarly, a few moderately taxed forced unionization states still had weak job growth (Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri). The combination of both a heavy tax burden and forced unionization is deadly when it comes to job growth, as 11 of the 15 worst performing states are ranked in the top 20 for high tax burdens.” If Ohio and the other states from Missouri to Maine want to truly compete with Texas, Georgia, and South Carolina, then those states need to enact laws that protect the rights of workers not to join a labor union to get a job.